What can companies do to spark innovation in the workplace?
As we leave behind the lockdowns and business disruptions of COVID-19 and enter a ‘new normal’, it is time to talk about how workplaces might be transformed to drive innovation.

As we leave behind the lockdowns and business disruptions of COVID-19 and enter a ‘new normal’, it is time to talk about how workplaces might be transformed to drive innovation.

Slovenians have fared comparatively well in terms of mental health during the COVID-19 pandemic compared to their EU counterparts standing at 53.2 on a scale of 100, behind only Denmark and Finland. According to Eurofound’s large-scale Living, working and COVID-19 online survey, the EU average was 45.3 in spring 2021.

74% of people in Croatia report difficulties making ends meet, according to Eurofound’s large-scale Living, working and COVID-19 online survey. This is the highest figure among EU Member States, where the average was 45.1%. For Croatia, this number remained consistently high throughout the pandemic at 73.5% in April 2020 reporting a difficult personal financial situation.

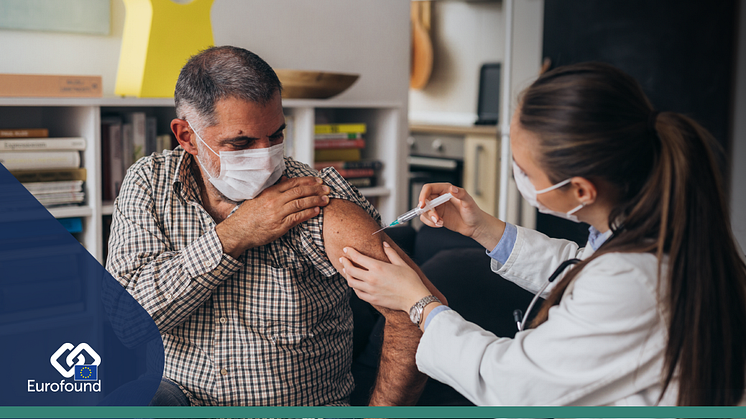
Vaccine acceptance is key to the success of COVID-19 vaccination campaigns worldwide. Worryingly, over a quarter of people living in Europe are hesitant about taking a COVID-19 vaccine, and the level of hesitancy is especially high among heavy users of social media.
The financial situation of people in Luxembourg is significantly better than the EU average with 11.3% of respondents reporting difficulties in making ends meet in February and March 2021, according to Eurofound’s large-scale Living, working and COVID-19 online survey. This is the third lowest figure among EU Member States with the EU average at 23.6%, just behind Denmark and Sweden.

Are there any lessons to be learnt about the factors that helped some organisations to navigate through the crisis more smoothly than others?

With its proposed directive on gender pay transparency, the European Commission has significantly bolstered the set of tools for delivering its objectives compared to those presented in its 2014 Recommendation. The proposed portfolio of measures addresses many shortcomings of the instruments that national authorities currently employ.

The economic uncertainty created by the COVID-19 pandemic slowed, but did not stop, overall minimum wage growth in the EU in 2021. Minimum wages were raised cautiously in most Member States, with the median country recording an increase of 3%. Only a few Member States froze their minimum wage rates, marking a very different approach to that taken in the aftermath of the 2008 financial crisis.

The trust of people in Portugal in the European Union is the highest across all Member States, according to Eurofound’s large-scale Living, working and COVID-19 survey. With 5.9, it is significantly higher than the EU average at 4.6. Trust in the EU in Portugal has increased throughout the COVID-19 pandemic from 5.2 in April 2020 to 5.4 during the summer of last year to 5.9 in spring 2021.

Decision-makers approached minimum wage setting for 2021 cautiously due to the economic uncertainty caused by the pandemic. Despite this, nominal statutory minimum wages rose in most Member States and the UK, although at lower rates than in recent years.

Throughout the COVID-19 pandemic, trust of people in Sweden in their national government has declined from 6.4 to 5.1. Respondents rated their trust levels at the onset of the pandemic (data collection April 2020) at 6.4 on average, which decreased to 5.5 during the summer months of last year and then to 5.1 in February and March of this year.

Trust in the national government in Denmark ranked highest among EU countries at 7 out of 10, according to Eurofound’s large-scale Living, working and COVID-19 online survey. This marked an increase of 0.5 points compared to the summer of last year. This pattern goes against the trend observed in all other EU Member States, where the average trust rating fell to just 3.9 from 4.6.
