Combating labour market segmentation in Europe
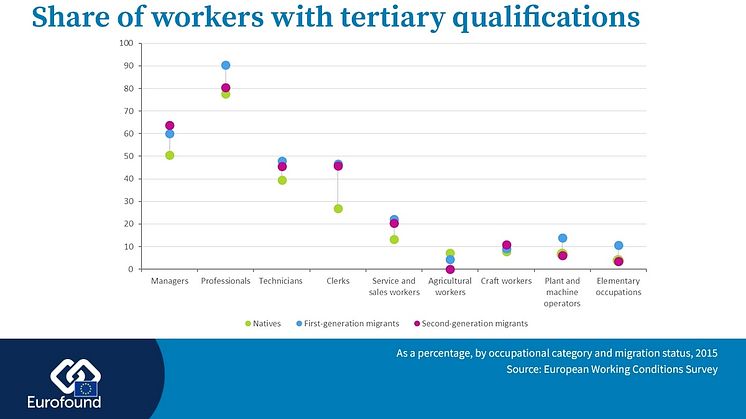
A common understanding of labour market segmentation is necessary to tackle poor quality jobs with lack of opportunities, affecting especially young people, women, immigrants and lower-educated individuals on the labour market. A new ambitious report explores why segmentation is problematic and identifies policy approaches which could be helpful in tackling this phenomenon.