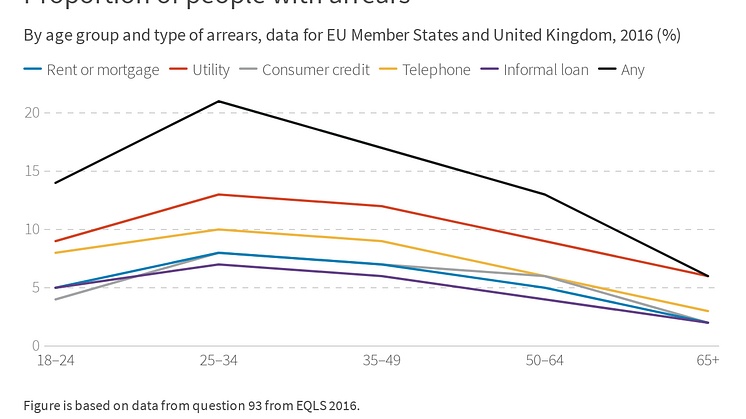
People aged 25-34 most likely to be in arrears
People aged 25-34 are most likely to be in arrears in the EU, according to Eurofound’s new report on Addressing household over-indebtedness. Among this age group, 21% of people surveyed in the 2016 European Quality of Life Survey reported being in some form of arrears.